Dengue Fever: Symptoms and Treatment | Complete Guide
Dengue fever, often called “breakbone fever,” is a mosquito-borne viral infection that affects millions of people globally, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. Caused by the dengue virus (DENV) and transmitted by the female Aedes aegypti mosquito, dengue can range from mild illness to severe life-threatening conditions.
In this blog, we will cover everything you need to know about dengue fever, its symptoms, treatment options, prevention tips, and recovery guidelines.
What is Dengue Fever?
Dengue fever is a viral infection spread through the bite of infected mosquitoes, primarily Aedes aegypti. It has become a major public health concern in Asia, Africa, the Caribbean, and Latin America.
There are four different types of dengue virus (DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3, DENV-4). A person can be infected multiple times, but subsequent infections increase the risk of severe dengue (dengue hemorrhagic fever).
How is Dengue Transmitted?
- Primary Carrier: Aedes aegypti mosquito.
- These mosquitoes are daytime biters, most active early morning and before sunset.
- They breed in stagnant water (coolers, water tanks, pots, discarded tires).
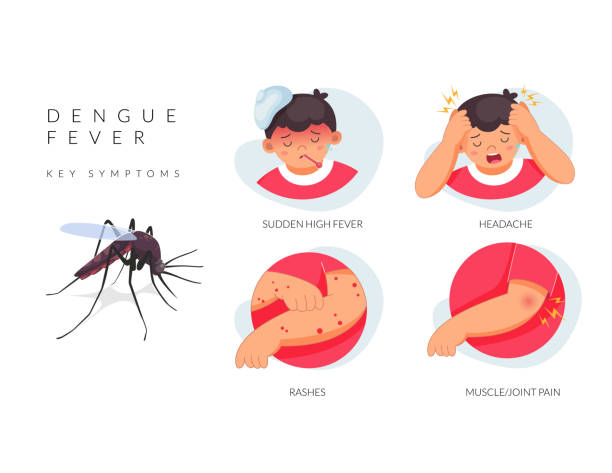
Symptoms of Dengue Fever
Dengue symptoms typically appear 4-10 days after the mosquito bite and last for 5-7 days. Symptoms can be mild or severe.
Common Symptoms:
- High fever (up to 104°F or 40°C)
- Severe headaches
- Pain behind the eyes
- Muscle, bone, and joint pain (breakbone pain)
- Skin rash (appears after 2-5 days of fever)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue and weakness
- Swollen glands
Severe Dengue (Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever) Symptoms:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Persistent vomiting
- Bleeding gums or nosebleeds
- Blood in vomit or stools (black tarry stools)
- Rapid breathing or difficulty breathing
- Cold, clammy skin (shock)
- Low platelet count leading to internal bleeding
Severe dengue can be life-threatening and requires immediate hospitalization.
Diagnosis of Dengue Fever
- Blood Tests to detect:
- Dengue NS1 antigen (early detection)
- Dengue IgM and IgG antibodies
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) to monitor platelets and white blood cells.
Early diagnosis helps in better management and avoiding complications.
Treatment of Dengue Fever
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment for dengue. Management is supportive and symptom-based.
1. Hydration:
- Drink plenty of fluids (ORS, coconut water, juices, soups).
- Prevent dehydration caused by high fever and vomiting.
2. Fever and Pain Management:
- Paracetamol (acetaminophen) is recommended to reduce fever and relieve pain.
- Avoid NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Aspirin) as they increase the risk of bleeding.
3. Rest and Monitoring:
- Complete bed rest is essential.
- Regular monitoring of platelet count and hematocrit levels.
4. Hospitalization (for severe dengue):
- Intravenous (IV) fluids for severe dehydration.
- Blood transfusions in case of severe bleeding.
- Oxygen therapy and intensive monitoring in critical cases.
Recovery from Dengue Fever
- Recovery generally takes 1-2 weeks.
- Fatigue and weakness may persist for several weeks post-infection.
- Light diet, plenty of fluids, and proper rest aid in recovery.
Complications of Dengue Fever
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF)
- Dengue Shock Syndrome (DSS)
- Organ damage (liver, heart)
- Low platelet-induced internal bleeding
Immediate medical care can reduce the risk of these complications.
Prevention of Dengue Fever
Since there’s no widely available vaccine for dengue in many countries, prevention is the best strategy.
1. Mosquito Control:
- Eliminate standing water in and around the home.
- Regularly clean water storage containers.
- Use mosquito nets, especially during daytime rest.
2. Personal Protection:
- Wear long-sleeved clothing and full-length pants.
- Apply mosquito repellents (DEET-based).
- Use window and door screens.
3. Community Measures:
- Participate in fogging drives and community awareness.
- Support local health authorities in mosquito control programs.
Home Remedies for Dengue Fever (Supportive Care)
While medical treatment is essential, some home remedies may help in supportive care:
- Papaya Leaf Extract: Believed to help increase platelet count.
- Giloy Juice (Tinospora Cordifolia): Boosts immunity.
- Turmeric Milk: Anti-inflammatory and boosts recovery.
- Pomegranate and Beetroot Juice: Helps replenish blood cells.
Note: Always consult a doctor before using home remedies.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can Dengue be fatal?
Yes, severe dengue can lead to life-threatening complications like bleeding, shock, and organ failure if not treated timely.
Q2. How long does dengue fever last?
Mild dengue fever usually lasts 5-7 days, but complete recovery may take 2 weeks.
Q3. Can a person get dengue more than once?
Yes, infection with one dengue serotype does not provide immunity against other serotypes. Subsequent infections can be more severe.
Q4. Is there a vaccine for dengue?
Some dengue vaccines (like Dengvaxia) exist but are not universally available and are recommended only in certain cases.
***************************************************************************************************
Conclusion
Dengue fever is a preventable yet serious disease. By following proper mosquito control measures, maintaining good hygiene, and staying alert to symptoms, you can protect yourself and your family from this viral threat. Early diagnosis and timely treatment are critical in managing dengue fever effectively.
Stay safe, stay healthy, and prevent dengue!
********************************************************************************
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dengue-and-severe-dengue
https://pram123.com/typhoid-fever-treatment-best-antibiotics-and-latest/
*********************************************************************************